Black Tar Spot
(Rhytisma acerinum)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Distribution • Taxonomy
|
|
|||||||||||||
Description |
Black Tar Spot is one of three species of parasitic fungi that infect several species of maple. Collectively the group is known by the common name Tar Spot of Maple. In Minnesota, Black Tar Spot, an introduced species, infects mostly Norway maple, another introduced species. However, it also infects several other species, including American Sycamore. In Europe, it is known by the common name Sycamore Tarspot. It is often found in suburban locations, where its host is planted. It is somewhat intollerant of air pollution. It does not grow in industrial areas where there are high levels of sulpher emissions. In the spring the infection appears as a yellow spot on the leaf. These turn first brownish-black with a yellow border, then, in late summer, black with a yellow border. The black spots resemble tar. The spots are solid, not a cluster of small spots. They may be up to 1½″ in diameter but are usually much smaller. |
Similar Species |
Speckled Tar Spot (Rhytisma punctatum) causes dense clusters of very small black spots. American Tar Spot (Rhytisma americanum) infects red maple and silver maple. |
Habitat and Hosts |
Norway maple |
Ecology |
Season |
Spring to fall |
Distribution |
||
|
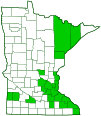
Sources Biodiversity occurrence data published by: Minnesota Biodiversity Atlas (accessed through the Minnesota Biodiversity Atlas Portal, bellatlas.umn.edu, 7/23/2025). Until 1998 this species name included what is now recognized as Rhytisma americanum. Some or all of the records represented on the map at left may be Rhytisma americanum. |
|
| 7/23/2025 | ||
Occurrence |
||
|
||
Taxonomy |
|
Kingdom |
Fungi (Fungi) |
Subkingdom |
Dikarya |
Phylum |
Ascomycota (Sac Fungi) |
Subphylum |
Pezizomycotina |
Class |
Leotiomycetes |
Order |
Rhytismatales |
Family |
Rhytismataceae |
Genus |
Rhytisma (tar spot fungi) |
The life cycle of this and most other fungi is pleomorphic. It has both an asexual reproductive phase (anamorph) and a sexual reproductive phase (telemorph). Each phase is often morphologically distinct. In the past, the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature allowed each phase to be assigned a different scientific name. It was incorrect to refer to the anamorph phase by the telemorph name, and vice versa. Some mycologists and molecular biologists consider this practice to be obsolete. Molecular phylogeny allows the accurate placement of a species in any part of their life cycle. On July 30, 2011, at the meeting of the XVIIIth International Botanical Congress in Melbourne, Australia, that practice ended. Prior to that meeting, the early, anamorphic phase of this fungi had been named Melasmia acerina. Both phases are now named Rhytisma acerinum. |
|
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
Melasmia acerina Xyloma acerinum |
|
Common Names |
|
Black Tar Spot European Tar Spot Sycamore Tarspot |
|
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this fungus. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||

Slideshows |
Rhytisma acerinum - fungi kingdom |
About
Published on Jan 25, 2015 Rhytisma acerinum - fungi kingdom |

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this fungus. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
Insights into Nature - Tar Spot Fungus on Sycamore |
About
Published on Oct 27, 2014 The Tar Spot (Rhytisma acerinum) is a very common ascomycete fungus that typically grows on Celtic Maple / Sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus) leaves giving a prominent black spot or spots on the leaf lamina, upper and lower epidermal surfaces. It is reported to grow occasionally on Norway Maple (Acer platanus) leaves. |

Visitor Sightings |
||
Report a sighting of this fungus. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
|
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
||
|

Created: 9/11/2015 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |