heart-leaved skullcap
(Scutellaria ovata ssp. ovata)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Conservation Status |
|
|||||||
| IUCN Red List | not listed |
|||||||
| NatureServe | N5 - Secure S2 - Imperiled |
|||||||
| Minnesota | Threatened |
|||||||
Wetland Indicator Status |
||||||||
| Great Plains | FACU - Facultative upland |
|||||||
| Midwest | FACU - Facultative upland |
|||||||
| Northcentral & Northeast | FACU - Facultative upland |
|||||||
Description |
||
Heart-leaved skullcap is an erect, perennial forb that rises on a single stem or a small cluster of stems from a slender underground stem (rhizome) and a fibrous root system. It may be 12″ to 31½″tall, but is usually between 16″ and 27½″ in height. It readily spreads by producing aboveground runners (stolons), and often forms small colonies of up to 50 plants. The stems are usually erect, sometimes ascending, four-angled (square), leafy, and usually unbranched below the inflorescence. They are densely covered with soft, spreading, gland-tipped hairs. The foliage is not aromatic. The leaves are opposite. The largest leaves are 2″ to 4½″ long and ¾″ to 3″ wide. They are on hairy, 5 ⁄16″ to 2″ long leaf stalks (petioles). The petioles are not winged at the tip. They become progressively smaller and shorter stalked as they ascend the stem. The leaf blades are heart-shaped to narrowly egg-shaped or triangular egg-shaped; heart-shaped, rounded, or squared off at the base; and usually sharply pointed, sometimes bluntly pointed, at the tip. They are pinnately veined. The veins are only slightly indented on the upper surface—they do not appear puckered. The upper and lower surfaces are densely covered with relatively long, spreading to curved, mostly gland-tipped hairs. The lower surface often also has unstalked glands. The margins are coarsely toothed with usually more than 12 teeth per side. The inflorescence is 1 to 3 slender, up to 4″ long arrangements (racemes) of flowers at the end of the stem. There are sometimes shorter racemes in the upper leaf axils. There are two opposite flowers at each node of the raceme. Each flower is on a short, slender stalk and is subtended by a single ⅛″ to ⅜″ long modified leaf (bract). The bracts are egg-shaped or broadly egg-shaped and ⅛″ to ⅜″ long, becoming shorter as flowers approach the tip. They do not extend beyond the whorl of sepals (calyx) of the flower which they subtend, except rarely late in the season. The bract on even the lowest flower is much smaller than the uppermost leaves. The flowers are ⅝″ to 1″ long. There are 5 sepals, 5 petals, 4 stamens, and 1 style. The sepals are whitish-green and ⅛″ to 3 ⁄16″ long in flower. They are united into a calyx tube at the base and separated into 2 shallow, broadly rounded lobes at the tip. They do not have a spine at the tip. They are densely covered with spreading, mostly gland-tipped hairs. The petals are mostly pale blue to bluish-purple. The outer surface of the corolla is densely covered with short, spreading, gland-tipped hairs. The petals are united at the base into a long, narrowly funnel-shaped tube and separated at the tip into 2 lips. The tube is usually white and is “S” shaped, bent upward just above the calyx, straight for most of its length, and curved at or above the throat. The is no ring of hairs in the throat. The upper lip is unlobed, and rounded. It forms a “skull”-shaped hood. The lower lip is white with blue spots or mottling, often has a narrow blue band at the margin, and is shallowly 3-lobed. It is spreading or arched, slightly longer than the upper lip, and deeply notched at the tip. The lateral lobes of the lower lip are short and ascending, not well developed. The lower lobe is broadly fan-shaped to semicircular and sometimes slightly notched. The stamens have small, pale yellow to white anthers and do not project beyond the corolla tube. The style is branched at the tip and does not project beyond the corolla tube. The fruit is a dry seed capsule (schizocarp) with 1 to 4 nutlets. The calyx becomes closed and ⅛″ to ¼″ long in fruit. |
||
Height |
||
16″ to 27½″ |
||
Flower Color |
||
Pale blue to bluish-purple and white |
||
Similar Species |
||
Blue skullcap (Scutellaria lateriflora) inflorescence is axillary racemes in upper leaf axils—there is no raceme at the end of the stem. The flowers are much smaller. Leonard’s skullcap (Scutellaria parvula var. missouriensis) is much smaller, no more than 12″ tall, usually 8″ or less. Leaf margins are untoothed and often curled under. It sometimes produces short, white, self-pollinating flowers. Marsh skullcap (Scutellaria galericulata) leaf margins have shallow, usually rounded teeth. The inflorescence is single flowers rising from the upper leaf axils. |
||
Habitat |
||
Dry to moderately moist. Upland and bottomland hardwood forests, woodland openings, bluffs. Loamy soil with limestone sand or rock. Full or partial shade. |
||
Ecology |
||
Flowering |
||
Late June to mid-August |
||
Pests and Diseases |
||
|
||
Use |
||
|
||
Distribution |
||||
|
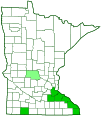
Sources Since 1984, only seven populations have been found in southeast Minnesota. The outlier in Stearns County (light green on the map) is an historical record from July, 1908. The outlier in Jackson County (dark green on the map) was found in a Minnesota Biological Survey vegetation releve sample plot on private property in 2001. |
|||
| 2/23/2023 | ||||
Nativity |
||||
Native |
||||
Occurrence |
||||
Rare in Minnesota |
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) | ||
| Subkingdom | Pteridobiotina | ||
| Phylum | Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) | ||
| Subdivision | Spermatophytina (Seed Plants) | ||
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicots) | ||
Order |
Lamiales (Mints, Plantains, Olives, and Allies) | ||
Family |
Lamiaceae (Mint) | ||
| Subfamily | Scutellarioideae | ||
| Genus | Scutellaria (skullcaps) | ||
| Species | Scutellaria ovata (heart-leaved skullcap) | ||
Synonyms |
|||
Scutellaria cordifolia Scutellaria ovata ssp. calcarea Scutellaria ovata ssp. mississippiensis Scutellaria ovata ssp. pseudovenosa Scutellaria ovata ssp. versicolor Scutellaria ovata var. calcarea Scutellaria ovata var. versicolor |
|||
Common Names |
|||
egg-leaf skullcap egg-leaved skullcap forest skullcap heart-leaved skullcap heartleaf skullcap ovate-leaved skullcap |
|||
Glossary
Axil
The upper angle where a branch, stem, leaf stalk, or vein diverges.
Bract
Modified leaf at the base of a flower stalk, flower cluster, or inflorescence.
Calyx
The group of outer floral leaves (sepals) below the petals, occasionally forming a tube.
Corolla
A collective name for all of the petals of a flower.
Glandular hairs
Hairs spread over aerial vegetation that secrete essential oils. The oils act to protect against herbivores and pathogens or, when on a flower part, attract pollinators. The hairs have a sticky or oily feel.
Node
The small swelling of the stem from which one or more leaves, branches, or buds originate.
Petiole
On plants: The stalk of a leaf blade or a compound leaf that attaches it to the stem. On ants and wasps: The constricted first one or two segments of the rear part of the body.
Pinnately veined
With the veins arranged like the vanes of a feather; a single prominent midvein extending from the base to the tip and lateral veins originating from several points on each side.
Raceme
An unbranched, elongated inflorescence with stalked flowers. The flowers mature from the bottom up.
Rhizome
A horizontal, usually underground stem. It serves as a reproductive structure, producing roots below and shoots above at the nodes.
Schizocarp
A dry fruit formed from a compound ovary that splits into two or more parts (mericarps) at maturity.
Sepal
An outer floral leaf, usually green but sometimes colored, at the base of a flower.
Stolon
An above-ground, creeping stem that grows along the ground and produces roots and sometimes new plants at its nodes. A runner.
Wing
A thin, flat, membranous, usually transparent appendage on the margin of a structure.
Visitor Photos |
|||||
Share your photo of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach one or more photos and, if you like, a caption. |
|||||
|
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|||||
|
|||||

Slideshows |
||

Visitor Videos |
|||
Share your video of this plant. |
|||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach a video, a YouTube link, or a cloud storage link. |
|||
Other Videos |
|||

Visitor Sightings |
|||||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Be sure to include a location. |
|||||
|
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
|||||
|
|||||

|
Created: Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |