Green plant bug
(Ilnacora malina)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Distribution • Taxonomy
Conservation Status |
|||
| IUCN Red List | not listed |
||
| NatureServe | not listed |
||
| Minnesota | not listed |
||
Description |
Plant bugs (family Miridae) is the largest family of true bugs (suborder Heteroptera). There are more than 10,000 known species worldwide, several hundred in North America. Green plant bug is a small true bug, a medium-sized to large plant bug. It occurs in the United States east of the Great Plains, from Vermont to Minnesota south to Missouri and Virginia, and in adjacent Canadian provinces. Based on the number of reported sightings in North America, it is not very common. Adults are soft-bodied, elongated, slender, almost parallel-sided, and 3 ⁄16″ to ¼″ (5 to 7 mm) in length. The head is wider than the base of hardened plate covering the first segment of the thorax (pronotum). The front of the head is almost vertical. The compound eyes are large and oval. There are no simple eyes (ocelli). The face and the top of the head are black. The beak-like part of the head containing the mouth parts (rostrum) has four segments. It is short, stout, and projects downward and forward when sucking plant juices. The neck is well defined. The antennae have four segments. They are thin and long, much longer than the head and as long as the entire thickened wing covers (hemelytra). The last half of the first segment and the entire second segment are black. The last two segments are much paler. The pronotum is wider than long and is bell-shaped when viewed from above. It is yellowish-green at the front, fading to green at the rear. It is sparsely covered with short white hairs. There is a round black spot on each side. There are two pairs of wings. They are held flat over the body when at rest. They are longer than and completely cover the body. The front wings (hemelytra) are longer than the hind wings. The exoskeletal plate between the wing bases (scutellum), is large, triangular, and green, with a depressed black spot in the middle at the base. The hemelytra have a thickened, leathery part at the base and a thin membranous part at the tip with a clear dividing line between the two. The thickened part is comprised of the narrow area (clavus) behind the scutellum when the wings are closed and the broad marginal area (corium). At the end of the corium there is a small but distinct triangular area (cuneus). The clavus, corium, and cuneus are green. There is a prominent dark streak in the middle of the clavus, a thinner streak in the corium, and a black spot in the cuneus. The membranous tip is dark black with yellow veins. It has two closed cells. The hind wing is completely thin and membranous. The legs are green, long, and delicate. The third leg segment (femur) is stout and somewhat flattened. The fourth segment (tibia) of the hind leg is very long. The end part of the leg (tarsus), corresponding to the foot, has 3 segments. The tips of the tibia and tarsi are brownish-black. |
Size |
Total length: 3 ⁄16″ to ¼″ (5 to 7 mm) |
Similar Species |
Habitat |
Damp, shady, grassy and weedy areas |
Ecology |
Season |
Mid-June to late July |
Behavior |
|
Life Cycle |
|
Nymph Food |
|
Adult Food |
Plant juices of giant ragweed and goldenrod. |
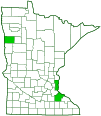
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 8/27/2025 | ||
Occurrence |
||
|
||
Taxonomy |
|
Order |
Hemiptera (True bugs, Hoppers, Aphids, and Allies) |
Suborder |
Heteroptera (True Bugs) |
Infraorder |
Cimicomorpha |
Superfamily |
Miroidea |
Family |
Miridae (Plant Bugs) |
Subfamily |
Orthotylinae |
Tribe |
Orthotylini |
Genus |
Ilnacora |
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
Sthenarops malina |
|
Common Names |
|
green plant bug |
|
Glossary
Cuneus
The triangular, hardened, horn-like tip of the forewing of a plant bug (family Miridae).
Femur
On insects and arachnids, the third, largest, most robust segment of the leg, coming immediately before the tibia. On humans, the thigh bone.
Hemelytron
The forewing of true bugs (order Hemiptera), thickened at the base and membranous at the tip. Plural: hemelytra.
Ocellus
Simple eye; an eye with a single lens. Plural: ocelli.
Pronotum
The exoskeletal plate on the upper side of the first segment of the thorax of an insect.
Rostrum
The stiff, beak-like projection of the carapace or prolongation of the head of an insect, crustacean, or cetacean.
Scutellum
The exoskeletal plate covering the rearward (posterior) part of the middle segment of the thorax in some insects. In Coleoptera, Hemiptera, and Homoptera, the dorsal, often triangular plate behind the pronotum and between the bases of the front wings. In Diptera, the exoskeletal plate between the abdomen and the thorax.
Tarsus
On insects, the last two to five subdivisions of the leg, attached to the tibia; the foot. On spiders, the last segment of the leg. Plural: tarsi.
Tibia
The fourth segment of an insect leg, after the femur and before the tarsus (foot). The fifth segment of a spider leg or palp. Plural: tibiae.
Visitor Photos |
Share your photo of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Alfredo Colon |
 |
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|

Slideshows |
|

Visitor Videos |
Share your video of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
|

|
Created: 6/15/2019 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |