hairy goldenrod
(Solidago hispida)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Conservation Status |
|
|||||||
| IUCN Red List | not listed |
|||||||
| NatureServe | N5 - Secure SNR - Unranked |
|||||||
| Minnesota | not listed |
|||||||
Description |
||
Hairy goldenrod is a 8″ to 40″ tall, erect, perennial forb that rises usually on a single stem from a branched caudex. It usually does not produce rhizomes and it does not form clumps. The stem is erect, unbranched, and leafy, with several fine, longitudinal ridges or grooves. It is moderately to densely covered with spreading hairs. Occasionally, the hairs are mostly appressed. Stem leaves are alternate. Basal and lower stem leaves are attached to the stem on a long winged leaf stalk (petiole). They are 2⅜″to 8″ long including the leaf stalk, and ½″ to 2⅜″ wide. The leaf blades are broad, inversely lance-shaped to inversely egg-shaped, with the attachment at the narrow end, or elliptic. They are tapered to the winged petiole at the base and taper to a sharp point at the tip with straight sides along the tip. There is one main vein. The margins may have sharp, forward-pointing teeth or rounded teeth, or they may be almost untoothed. The upper and lower surfaces are moderately to densely covered with spreading hairs. Occasionally, the hairs are mostly appressed. Basal leaves are usually present at flowering. There is often an additional rosette of basal leaves on the ground near the stem. Middle and upper stem leaves are lance-shaped to elliptic or inversely egg-shaped. They are ⅝″ to 3″ long, becoming rapidly smaller as they ascend the stem. They are attached to the stem without a leaf stalk. The margins on the leaves near the top of the stem are untoothed. The inflorescence is a branched cluster of short, unbranched clusters (racemes) rising from the upper leaf axils. The close spacing of the upper leaf axils and the shortness of the racemes combine to give the inflorescence the appearance of a spike at the end of the stem. This false spike can be 10″ or more long and have 8 to 250 or more flower heads. The flower heads in the the racemes are oriented in several directions. Each flower head has 6 to 14 yellow ray florets and 6 to 12 yellow disk florets. |
||
Height |
||
8″ to 40″ |
||
Flower Color |
||
Yellow ray flowers, yellow disk flowers |
||
Similar Species |
||
Habitat |
||
Moderate moisture to dry. Woods, roadsides. Full or partial sun. |
||
Ecology |
||
Flowering |
||
July to October |
||
Pests and Diseases |
||
|
||
Use |
||
|
||
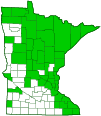
Distribution |
||||
|
Sources |
|||
| 4/14/2023 | ||||
Nativity |
||||
Native |
||||
Occurrence |
||||
|
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) | ||
| Subkingdom | Pteridobiotina | ||
| Phylum | Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) | ||
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicots) | ||
Order |
Asterales (Sunflowers, Bellflowers, Fanflowers, and Allies) | ||
Family |
Asteraceae (Sunflowers, Daisies, Asters, and Allies) | ||
| Subfamily | Asteroideae | ||
| Supertribe | Asterodae | ||
| Tribe | Astereae (asters and allies) | ||
| Subtribe | Solidagininae | ||
| Genus | Solidago (goldenrods) | ||
| Subgenus | Solidago | ||
| Section | Erectae | ||
| Subsection | Erectae | ||
Subordinate Taxa |
|||
Up to six varieties have been described based on pubescence and other minor variations. Most taxonomists do not recognize any varieties. |
|||
Synonyms |
|||
Solidago bicolor var. concolor Solidago bicolor var. lanata Solidago bicolor var. ovalis Solidago bicolor var. tonsa Solidago hispida var. arnoglossa Solidago hispida var. hispida Solidago hispida var. lanata Solidago hispida var. tonsa |
|||
Common Names |
|||
hairy goldenrod |
|||
Glossary
Axil
The upper angle where the leaf stalk meets the stem.
Caudex
A short, sometimes woody, persistent stem, at or below ground level, from which aerial stems arise each year.
Petiole
On plants: The stalk of a leaf blade or a compound leaf that attaches it to the stem. On ants and wasps: The constricted first one or two segments of the rear part of the body.
Raceme
An unbranched, elongated inflorescence with stalked flowers. The flowers mature from the bottom up.
Winged leaf stalk
A leaf stalk with a leaf-like or membrane-like extension along both sides.
Visitor Photos |
|||||
Share your photo of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach one or more photos and, if you like, a caption. |
|||||
Luciearl |
|||||
 |
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|||||
Plant |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
 |
|||||
Inflorescence |
|||||
 |
|||||
Leaves |
|||||
 |
 |
||||

Visitor Videos |
|||
Share your video of this plant. |
|||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach a video, a YouTube link, or a cloud storage link. |
|||
Other Videos |
|||


|
Created: Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |