Amur maple - Species Profile
Conservation • Weed • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
||
Amur maple is a moderately fast-growing, moderately long-lived, deciduous, large shrub or small tree. It usually rises on multiple stems, forming a 10′ to 20′ in height, wider than tall shrub. Sometimes it rises on a single trunk, taking the form of a tree up to 26′ tall and up to 12″ in diameter at breast height. When the plant is a tree, the trunk is distinct only to the base of the crown. The branches are spreading. The crown is rounded. The bark on young trees and stems is grayish-brown, thin, smooth, and marked with fine parallel lines. On mature trees the bark is rough and shallowly furrowed. On older trees the bark is separated into long, thin plates. The twigs are slender, light brown to yellowish-brown or reddish-brown, and hairless. They are round in cross section and have solid, pale to white pith. The leaf scars are crescent-shaped and have three bundle scars. Leaf scars on opposite sides of the twig are joined by a horizontal line. At the end of the twig is a brown, hairless, 1 ⁄16″ to ⅛″ long, rounded or blunt terminal bud with usually 4 overlapping scales. The scales have red to orange tips. Lateral buds are egg-shaped and have 2 or 4 overlapping outer scales that obscure 2 inner scales. The leaves are deciduous, opposite, broadly triangular egg-shaped in outline, ¾″ to 3″ long, and 1¼″ to 2½″ wide. They are on 1¼″ to 2″ long leaf stalks (petioles). When cut, the petioles exude a clear sap. There are no prominent stipules at the base of the petiole. The leaf blades are cut into 3 lobes, sometimes with two additional short lobes. The lobes taper to a sharp point at the tip and have V-shaped sinuses between them. The two lateral lobes are cut ⅓″ to ½″ of the way to the base. The central (terminal) lobe is usually much longer than the lateral lobes and is widest at or just above the base. The upper surface is green and shiny. The lower surface is paler green and either completely hairless or hairy just along the main veins. The margins are coarsely and irregularly toothed, sometimes double-toothed. In autumn the leaves turn yellow to red. The inflorescence is an erect, branched, spreading cluster (panicle) of many flowers at the tips of the branches. The panicles are on long stalks and appear during or after leaf out in May to June. Male and female flowers are borne on the same tree. Each flower has 4 sepals and 4 petals. The sepals are whitish green. They are fused only at the very base then separated into 4 oblong-elliptic, rounded lobes. The petals are yellowish-white, narrowly spoon-shaped, and 1 ⁄32″to 1 ⁄16″ long. Male flowers have usually 8, sometimes 7 stamens. Females have a densely hairy ovary, 1 pistil, and 2 styles. The flowers are fragrant. The fruit is a pair of dry seed cases (keys) with papery wings attached (double samara). They occur in clusters that droop downward from short stalks. They are slightly spreading, sometimes appearing almost parallel to each other. Individual keys are plump, ¾″ to 1⅜″ long, attached the the stalk, and slightly connected to each other. The wings alone are typically ⅝″ to 1 3 ⁄16″ long. The keys are hairless or sparsely hairy and green initially. The wings turn reddish when the seeds are mature. The keys turning brown in the fall. They drop in late fall just before the leaves. Paired keys remain united when they are shed. |
||
Height |
||
10′ to 26′ |
||
Record |
||
There is no record for nonnative species |
||
Flower Color |
||
Yellowish-white |
||
Similar Species |
||
Habitat |
||
Moist but well drained soil. Drought tolerant. Disturbed forest sites, old fields. Full sun to partial shade. Shade tolerant. |
||
Ecology |
||
Flowering |
||
May |
||
Pests and Diseases |
||
|
||
Use |
||
Amur maple has been widely sold as an ornamental, a windbreak, or a hedge or screen. |
||
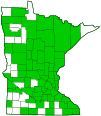
Distribution |
||||
|
Sources |
|||
| 2/16/2023 | ||||
Nativity |
||||
Native to Mongolia, China, Russia, and North Korea. Introduced into North America in the 1860s. It has escaped cultivation and is now naturalized. |
||||
Occurrence |
||||
|
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) | ||
| Subkingdom | Pteridobiotina | ||
| Phylum | Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) | ||
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicots) | ||
Order |
Sapindales (Soapberries, Cashews, Mahoganies, and Allies) | ||
Family |
Sapindaceae (Soapberry) | ||
| Subfamily | Hippocastanoideae | ||
| Tribe | Acereae | ||
Genus |
Acer (Maples) | ||
| Section | Ginnala | ||
Synonyms |
|||
Acer tataricum ssp. ginnala |
|||
Common Names |
|||
Amur maple ginnala maple |
|||
Glossary
Bundle scar
Tiny raised area within a leaf scar, formed from the broken end of a vascular bundle.
Panicle
A pyramidal inflorescence with a main stem and branches. Flowers on the lower, longer branches mature earlier than those on the shorter, upper ones.
Petiole
On plants: The stalk of a leaf blade or a compound leaf that attaches it to the stem. On ants and wasps: The constricted first one or two segments of the rear part of the body.
Sepal
An outer floral leaf, usually green but sometimes colored, at the base of a flower.
Pith
The spongy cells in the center of the stem.
Samara
A dry fruit consisting of a seed attached to a papery wing; one seeded in Elms and Ashes, two-seeded in Maples.
Stipule
A small, leaf-like, scale-like, glandular, or rarely spiny appendage found at the base of a leaf stalk, usually occurring in pairs and usually dropping soon.