northern starflower
(Lysimachia borealis)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
Northern starflower is a 4″ to 8″ tall, erect, perennial forb that rises on a single stem from a long, slender, creeping rhizome and fibrous roots. The stems are erect, slender, unbranched, round in cross section, and hairless. There is a whorl of 5 to 9 leaves at the top of the stem and usually one or more much smaller leaves between the middle and the top of the stem. The leaves in the whorl are short-stalked or stalkless, lance-shaped to lance-elliptic, ¾″ to 4″ long, ¼″ to 1¾″ wide, and widest at the middle. They are narrowly wedge-shaped at the base and taper to a point at the tip with straight or concave sides along the tip. They are pinnately veined with a single prominent midvein and several lateral veins that join at the end and do not reach the margin. The upper and lower surfaces are hairless. The margins are untoothed. The leaves lower on the stem, if any, are alternate, inconspicuous, 1 ⁄32″ to ¼″ long, 1 ⁄32″to 1 ⁄16″ wide, and often more or less scale-like. The inflorescence is usually 1, sometimes 2 or 3 flowers rising from the upper leaf axils. Each flower is solitary at the end of slender flower stalk (pedicel). The pedicel is hairless but sparsely covered with stalked glands. It is ¾″ to 2″ long, usually shorter than the leaves. The flower is 5 ⁄16″ to 9 ⁄16″ wide, flat, and circular. There are 5 to 9, usually 7 sepals, 5 to 9, usually 7 petals, and 5 to 9, usually 7 stamens. The sepals are green and are fused at the base into a short calyx tube, then separated into lance-shaped or lance-linear lobes that are longer than the tube. The petals are white and are fused at the base into a short corolla tube, then separated into widely spreading, egg-shaped to narrowly lance-shaped lobes that are longer than the tube. The petals are longer than the sepals and are pointed at the tip. The stalks of the stamens (filaments) are fused at the base. The fruit is an globe-shaped capsule. It ripens in mid-summer. |
Height |
4″ to 8″ |
Flower Color |
White |
Similar Species |
| No similar species |
Habitat |
Moist. Coniferous forests, mature hardwood forests, bogs. Light shade. |
Ecology |
Flowering |
May to June |
Pests and Diseases |
|
Use |
|
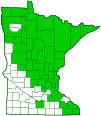
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 5/29/2025 | ||
Nativity |
||
Native |
||
Occurrence |
||
Common |
||
Taxonomy |
|
Kingdom |
|
Subkingdom |
Pteridobiotina |
Phylum |
Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) |
Class |
|
Order |
Ericales (heathers, balsams, primroses, and allies) |
Family |
Primulaceae (primrose) |
Subfamily |
Myrsinoideae (cape myrtle) |
Genus |
Lysimachia (loosestrifes) |
Section |
Trientalis (starflowers) |
Starflowers were formerly placed in the genus Trientalis, which was part of the Lysimachia complex. A recent phylogenetic analysis (Manns & Anderberg, 2009) concluded that the genus Trientalis is invalid, and the species were moved to the genus Lysimachia, section Trientalis. |
|
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
Trientalis americana Trientalis borealis Trientalis borealis ssp. borealis |
|
Common Names |
|
American starflower northern starflower starflower |
|
Glossary
Calyx
The group of outer floral leaves (sepals) below the petals, occasionally forming a tube.
Corolla
A collective name for all of the petals of a flower.
Filament
On plants: The thread-like stalk of a stamen which supports the anther. On Lepidoptera: One of a pair of long, thin, fleshy extensions extending from the thorax, and sometimes also from the abdomen, of a caterpillar.
Pinnately veined
With the veins arranged like the vanes of a feather; a single prominent midvein extending from the base to the tip and lateral veins originating from several points on each side.
Rhizome
A horizontal, usually underground stem. It serves as a reproductive structure, producing roots below and shoots above at the nodes.
Sepal
An outer floral leaf, usually green but sometimes colored, at the base of a flower.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Luciearl |
||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
 |
 |
|
 |

Slideshows |
Starflower (Trientalis borealis) |

|
About
Primrose Family |
Trientalis borealis (Star-Flower) |

|

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
MyNature Apps; Identifying Starflower, Trientalis borealis |
About
Uploaded on May 30, 2011 How to identify Starflower, Trientalis borealis also known as May Star, Star-of-Bethlehem and Broadleaf starflower. www.mynatureapps.com |

Visitor Sightings |
||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Luciearl |
Location: Fairview Twp. |
 |
| Luciearl 5/28/2020 |
Location: Fairview Twp, Cass County |
 |
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
||

|
Created: 6/9/2013 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |