white oak
(Quercus alba)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
||
White oak is a slow growing, deciduous tree rising on a single trunk from a deep, fibrous root system with well-developed, tapered laterals. It is very long lived, often surviving 500 to 600 years. In Minnesota mature trees are usually 50′ to 70′ tall and up to 40″ in diameter, though individuals can reach 100′ in height. In open areas the crown is irregular and widespread with many gnarled and twisted, widely spreading branches. The trunk is stocky and is distinct well into the crown. In forests the crown is upright and oval. The bark on mature trees is relatively thin and ashy gray, with irregular, scaly blocks on smaller stems or narrow flat-topped ridges and shallow furrows on larger stems. The twigs are moderately stout. They are green to reddish-green and hairy when young, becoming gray and hairless as they age. Terminal buds are dark reddish-brown, hairless, egg-shaped, and ⅛″ to 3 ⁄16″ long. They are round, not angled, in cross section. They appear in a cluster at the end of the twig. Lateral buds diverge from the twig. The leaves are alternate, oblong to egg-shaped in outline, 4″ to 6¾″ long, and 2⅜″ to 4¾″ wide. They are on hairless or almost hairless, ⅜″ to 1″ long leaf stalks. The leaf blade is narrowly wedge-shaped or angled at the base and rounded at the tip. There are 2 or 3 often narrow primary lobes separated by narrow, shallow or deep sinuses and 0 to 5 smaller, secondary lobes per side. The deepest sinuses extend 50% to 95% of the way to the midrib. The upper surface is green, dull or shiny, and hairless. The lower surface is light green, hairless or with a few reddish, appressed hairs along the main veins. In autumn the leaves turn yellow, red, or purplish-brown. Male and female flowers are borne on the same branch. Male flowers are in slender, greenish, 1¼″ to 3″ long catkins that hang downward from buds on branchlets of the previous year. Female flowers are bright green and appear singly or in clusters of 2 or 3 on a short stalk rising from leaf axils on branchlets of the current year. The flowers appear after the leaves in early to late May. The fruit is an ellipsoidal or egg-shaped, ⅝″ to 1″ long, 7 ⁄16″ to ⅝″ wide acorn. It occurs singly or in clusters of 2 or 3 on a short, stout stalk. A scaly, broadly bowl-shaped cup encloses ¼ to⅓ of the lower part of the nut. The scales on the cup have a prominent, warty bump and the tips of the scales are free. The kernel is light brown. It ripens in mid-August to late September of the first year. |
||
Height |
||
50′ to 70′ |
||
Record |
||
The champion white oak in Minnesota is on private property near Belle Plaine, in Scott County. In 2002 it was measured at 72′ tall and of 201″ in circumference (64″ in diameter), with a crown spread of 84′. |
||
Flower Color |
||
Green |
||
Similar Species |
||
Bur oak (Quercus macrocarpa var. macrocarpa) bark is thick and deeply furrowed. The branchlets have corky ridges. The lateral are closely appressed to the twig. The leaves are variable in shape and often have a large terminal lobe. The acorn cup encloses ½ to ⅞ or more of the nut, and has a fringe of awns along the rim. |
||
Habitat |
||
Moist to moderately dry; very drought tolerant. Deciduous forests. Moderately shade tolerant. |
||
Ecology |
||
Flowering |
||
May to early June |
||
Pests and Diseases |
||
|
||
Use |
||
|
||
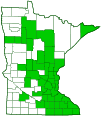
Distribution |
||||
|
Sources |
|||
| 7/7/2023 | ||||
Nativity |
||||
Native |
||||
Occurrence |
||||
Common |
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) | ||
| Subkingdom | Pteridobiotina | ||
| Phylum | Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) | ||
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicots) | ||
Order |
Fagales (Beeches, Oaks, Walnuts, and Allies) | ||
Family |
Fagaceae (Beech) | ||
| Subfamily | Fagoideae | ||
Genus |
Quercus (oak) | ||
| Subgenus | Quercus | ||
| Section | Quercus (white oak) | ||
Subordinate Taxa |
|||
|
|||
Synonyms |
|||
Quercus alba var. subcaerulea Quercus alba var. subflavea |
|||
Common Names |
|||
white oak |
|||
Glossary
Catkin
A slim, cylindrical, drooping cluster of many flowers. The flowers have no petals and are either male or female but not both.
Visitor Photos |
|||||
Share your photo of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach one or more photos and, if you like, a caption. |
|||||
|
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|||||
Bark |
|||||
 |
|||||
Leaves |
|||||
 |
|||||
Infructescence |
|||||
 |
|||||

Slideshows |
||
| Quercus alba Blake C. Willson |
||

|
||
About
White |
||
| White Oak J.Steinbock |
||

|
||
| Quercus alba - White Oak Virens (Latin for greening) |
||

|
||
About
Fagaceae - Beech Family. A New York City street tree native to North America. For a description of leaf identification features of White Oak, the flagship member of the White Oak Group, please consult: |
||
| White oak Jim Hamilton |
||
About
Uploaded on Jun 20, 2008 A brief species overview of white oak (Quercus alba). |
||

Visitor Videos |
|||
Share your video of this plant. |
|||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach a video, a YouTube link, or a cloud storage link. |
|||
Other Videos |
|||
| Trees with Don Leopold - white oak ESFTV |
|||
About
Uploaded on Oct 21, 2011 |
|||
| Differences Between White Oak and Red Oak Trees for Whitetail Deer HuntingForReal |
|||
About
Published on Aug 21, 2012 Special guest and good friend, Brent Sawyer from Sawyer Consulting shares with us a wealth of knowledge on how to tell the difference between different Red and White Oak trees, and how they benefit deer. Have fun, be safe, shoot straight! |
|||
| Red Oak vs White Oak Windwalker's Outdoor Channel |
|||
About
Published on Aug 29, 2014 Here is a video showing how to tell the difference between red oak and white oak. Most deer hunters know that deer prefer white oak acorns over red oak acorns. Here is how to tell the difference so you can find a better place to hunt. |
|||
| White Oak Tree Pat Rick |
|||
About
Uploaded on Sep 9, 2009 http://www.tytyga.com/White-Oak-p/whi... White Oak Tree is a great tree plant to pass down to generations. The quick growing shade tree will be bring hours of entertainment. Plant a White Oak Tree today. |
|||
| White Oak Shade Tree aaronsbulb |
|||
About
Uploaded on Dec 12, 2009 http://www.aaronsfarm.com/White-Oak-p/white-oak-tree.htm |
|||

Visitor Sightings |
|||||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Be sure to include a location. |
|||||
|
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
|||||

|
Created: Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |