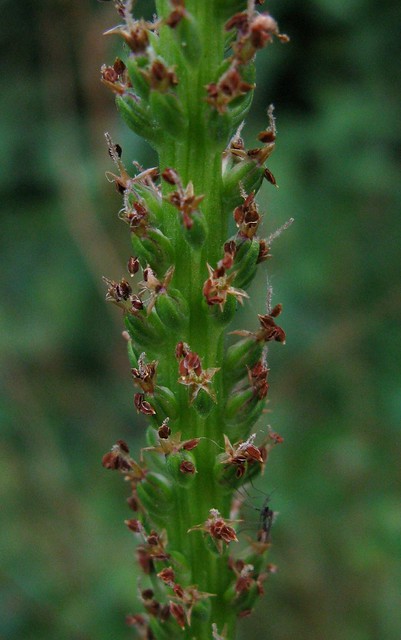
common plantain
(Plantago major)
Conservation • Weed • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
Common plantain is an exotic, very common, turfgrass weed. It is native to Europe, northern and central Asia, and northern and southern Africa. Evidence suggests that it was introduced in the early 1600s by Puritan colonists. It is one of the first plants to become established in North America following European arrival. Common plantain is a 3″ to 12″ tall, erect, perennial forb that rises on a rosette of leaves and 1 or more flowering stalks (scapes) from fibrous roots. The leaves are all basal and form a rosette. They are broadly elliptic to broadly egg-shaped, 1½″ to 7″ long, and ⅝″ to 4⅓″ wide, 1.3 to usually 2 times as long as wide. They have 3 or more prominent veins that separate at the base and are parallel to the margins. They are abruptly contracted at the base to the leaf stalk. The leaf stalk is hairless and entirely green, even at the base. The margins are untoothed or irregularly toothed. The scapes are leafless and 2″ to 10″ tall. The inflorescence is an unbranched, cylindrical spike of tiny green flowers at the end of the scape. The spikes narrow, tapering, hairless, 2″ to 11¾″ tall, and less than ⅜″ wide. The flowers are 1 ⁄16″ to ⅛″ long. There are 4 green to white petals, 4 sepals, and 4 stamens. They are subtended by 1 ⁄16″ to ⅛″ long, keeled, broadly egg-shaped, leaf-like bracts. Pollination is by wind. The fruit is a capsule containing 6 to 30 seeds. |
Height |
3″ to 12″ |
Flower Color |
Green to white |
Similar Species |
Black-seeded plantain (Plantago rugelii var. rugelii) has leaf stalks that are reddish at the base. The bracts are lance-shaped to triangular. |
Habitat |
Disturbed sites, gardens, lawns. |
Ecology |
Flowering |
June to August |
Pests and Diseases |
|
Use |
|
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 5/16/2024 | ||
Nativity |
||
Native to Europe, Asia, and Africa. Naturalized worldwide |
||
Occurrence |
||
Very common and widespread |
||
Taxonomy |
|
Kingdom |
|
Subkingdom |
Pteridobiotina |
Phylum |
Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) |
Class |
|
Order |
Lamiales (Mints, Plantains, Olives, and Allies) |
Family |
Plantaginaceae (plantain) |
Tribe |
Plantagineae |
Genus |
Plantago (plantains) |
Subgenus |
Plantago |
| Section | |
Subordinate Taxa |
|
common plantain (Plantago major ssp. intermedia) common plantain (Plantago major ssp. major) common plantain (Plantago major ssp. winteri) |
|
Plantago major ssp. intermedia is often treated as the separate species Plantago uliginosa. Flora of North America contends that detailed morphologic and genetic studies are needed before it can be determined which subspecies are present in North America and exactly where they occur. |
|
Synonyms |
|
Plantago adriatica Plantago altissima Plantago angustata Plantago borysthenica Plantago bracteata Plantago compressiscapa Plantago crenata Plantago dentata Plantago dilatata Plantago dostalii Plantago dregeana Plantago exaltata Plantago fonticola Plantago gigas Plantago gouanii Plantago gracilis Plantago humifusa Plantago jehohlensis Plantago jepohlensis Plantago laciniosa Plantago latifolia Plantago limosa Plantago longiscapa Plantago loureiroi Plantago majo ssp. fma Plantago major f. bifida Plantago major f. bracteata Plantago major f. brevipedicellata Plantago major f. crispa Plantago major f. dilatata Plantago major f. dostalii Plantago major f. dura Plantago major f. erecta Plantago major f. lancifolia Lepage Plantago major f. latissima Plantago major f. major Plantago major f. maxima Plantago major f. megasperma Plantago major f. megastachya Plantago major f. minima Plantago major f. minor Plantago major f. nervata Plantago major f. ovata Plantago major f. pleiosperma Plantago major f. pygmaea Plantago major f. rocae Plantago major f. rotundata Plantago major f. scopulorum Plantago major f. sinuata Plantago major f. vulgaris Plantago major ssp. asiatica Plantago major ssp. dostalii Plantago major ssp. gigas Plantago major ssp. kimurae Plantago major ssp. pachyphylla Plantago major ssp. pachystachya Plantago major ssp. pilgeri Plantago major ssp. rigidifolia Plantago major ssp. sinuata Plantago major var. agrestis Plantago major var. altissima Plantago major var. angustata Plantago major var. angustifolia Plantago major var. angustissima Plantago major var. borysthenica Plantago major var. brasiliensis Plantago major var. compressiscapa Plantago major var. crispa Plantago major var. dentata Plantago major var. desertica Plantago major var. dilatata Plantago major var. dostalii Plantago major var. dumanii Plantago major var. elatior Plantago major var. fastigiata Plantago major var. flavovirens Plantago major var. gigas Plantago major var. glaberrima Plantago major var. glabra Plantago major var. intermedia Plantago major var. japonica Plantago major var. jehohlensis Plantago major var. kimurae Plantago major var. lanceolata Plantago major var. latifolia Plantago major var. luxuriosa Plantago major var. macropoda Plantago major var. major Plantago major var. maxima Plantago major var. megastachya Plantago major var. microstachya Plantago major var. minima Plantago major var. minor Plantago major var. monstrosus Plantago major var. nana Plantago major var. pachyphylla Plantago major var. pachystachya Plantago major var. paludosa Plantago major var. paniculata Plantago major var. pauciflora Plantago major var. phyllostachya Plantago major var. pilgeri Plantago major var. pilosiuscula Plantago major var. polystachya Plantago major var. procera Plantago major var. pubescens Plantago major var. pygmaea Plantago major var. racemosa Plantago major var. ramosa Plantago major var. rhodostachya Plantago major var. rigidifolia Plantago major var. rosea Plantago major var. rubra Plantago major var. runcinata Plantago major var. sawadae Plantago major var. sawadai Plantago major var. scopulorum Plantago major var. sinuata Plantago major var. tropica Plantago major var. uliginosa Plantago major var. ungavensis Plantago major var. vivipara Plantago major var. vulgaris Plantago maxima Plantago media var. procera Plantago minima Plantago minor Plantago nana Plantago officinarum Plantago pauciflora Plantago polystachia Plantago quinquenervis Plantago rocae Plantago rosea Plantago sawadae Plantago sawadai Plantago sinuata Plantago sorokini Plantago stylosa Plantago subsinuata Plantago tabernaemontani Plantago villifera Plantago vulgaris Plantago winteri |
|
Common Names |
|
broad-leaved plantain buckhorn plantain common plantain grand plantain greater plantain plantain nipple-seed plant |
|
|
||
|
||
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Luciearl |
||
 |
||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |

Slideshows |
Greater Plantain |

|
About
Greater Plantain (Plantago major). |
Plantago major |
About
Uploaded on May 17, 2011 · Plants of future (http://www.pfaf.org)· GRIN - Taxonomic information (http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/taxfam.pl?language=es) |

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
Broadleaf Plantain (Plantago major) ~ LuminEarth's How to Identify Wild Edible & Medicinal Plants |
About
Uploaded on Sep 17, 2010 Broadleaf Plantain grows from a short, tough rootstock or rhizome, which has a large number of long, straight, yellowish roots, is a basal, rosette of large, broadly oval, dark green, leaves. The 4 to 10 inch long smooth, thick, strong and fibrous leaves have 3 to 7 or more ribbed veins, abruptly contracting into a long, petiole (leaf stalk) which is reddish at the base. The leaf margin of Broadleaf Plantain is entire, or unevenly toothed. The flower stalks, are erect, long, slender, densely-flowered spikes. Each tiny flower is brownish and bell-shaped with four stamens and purple anthers. Flowers bloom most of the summer. The fruit is a two-celled capsule and containing four to sixteen seeds. Gather young edible Broadleaf Plantain leaves in spring. Gather Plantain after flower spike forms, dry for later herb use. The young leaves of the Broadleaf Plantain plant are edible as a raw salad or cooked as spinach. Broadleaf Plantain contains Acubin which is reported to be a powerful anti-toxin. The leaves and the seed are medicinal used as an antibacterial, antidote, astringent, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antitussive, cardiac, demulcent, diuretic, expectorant, haemostatic, laxative, ophthalmic, poultice, refrigerant, and vermifuge. Medical evidence exists to confirm uses as an alternative medicine for asthma, emphysema, bladder problems, bronchitis, fever, hypertension, rheumatism and blood sugar control. For the most current and detailed information on this plant, please visit our FREE Online Guide to Wild Edible & Medicinal Plants at http://www.luminearth.com/luminearthsguide/ . Disclaimer: The statements in these videos are for educational purposes only and have not been evaluated by or sanctioned by the FDA. Only your doctor can properly diagnose and treat any disease or disorder. The remedies discussed herein are not meant to treat or cure any type of disease. The user understands that the above information is NOT intended as a substitute for the advice of a physician or a pharmacist. Make sure you can positively identify a plant before ingesting it. Some plants are poisonous, and misidentification could possibly result in serious illness or death. |
Greater Broadleaf Plantain (Plantago Major subsp. Major) - 2012-07-15 |
About
Published on Jul 18, 2012 Plantago major ("broadleaf plantain" or "greater plantain") is a species of Plantago, family Plantaginaceae. --------------------- |
Day Hike ( part 3 ) Common Plantain |
About
Uploaded on Jul 28, 2010 It is suggested by many authors and online resources that Common plantain is a good cure for poison ivy and insect bites. I have not found that to be the case. the young leaves are edible, but can be stringy. I personally don't like the flavor, but it is a good plant to become familiar with. |

Visitor Sightings |
||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Luciearl |
Location: Lake Shore, MN |
 |
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
||
Carpenter St. Croix Valley Nature Center Charles A. Lindbergh State Park Felton Prairie SNA, Bicentennial Unit Forestville/Mystery Cave State Park Itasca Wilderness Sanctuary SNA Lake Alexander Woods SNA, South Unit Minnesota Valley NWR, Chaska Unit Minnesota Valley NWR, Louisville Swamp Unit Minnesota Valley NWR, Rapids Lake Unit Mound Spring Prairie SNA, North Unit Northern Tallgrass Prairie NWR, Pavia Unit Northern Tallgrass Prairie NWR, Touch the Sky Prairie Unit Richard M. & Mathilde Rice Elliott SNA Sand Prairie Wildlife Management and Environmental Education Area Spring Beauty Northern Hardwoods SNA |

|
Created: Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |